
- Meaning Of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Causes Of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Risk Factors Of Ectopic Pregnancy (Who Is At Risk Of Ectopic Pregnancy?)
- Signs And Symptoms Of Ectopic Pregnancy
- How Is An Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
- Treatments Of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Can You Get Pregnant After An Ectopic Pregnancy?
- FAQs By Patients
Meaning Of Ectopic Pregnancy
Uterus is the only site where normally a fertilized egg implants (attaches) and grows by absorbing the nourishment from the mother’s blood and changes into a fully grown baby. But sometimes the fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity. When a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus the condition is known as an ectopic pregnancy. It is also known as an extrauterine pregnancy.
(Ectopic = In an abnormal place)
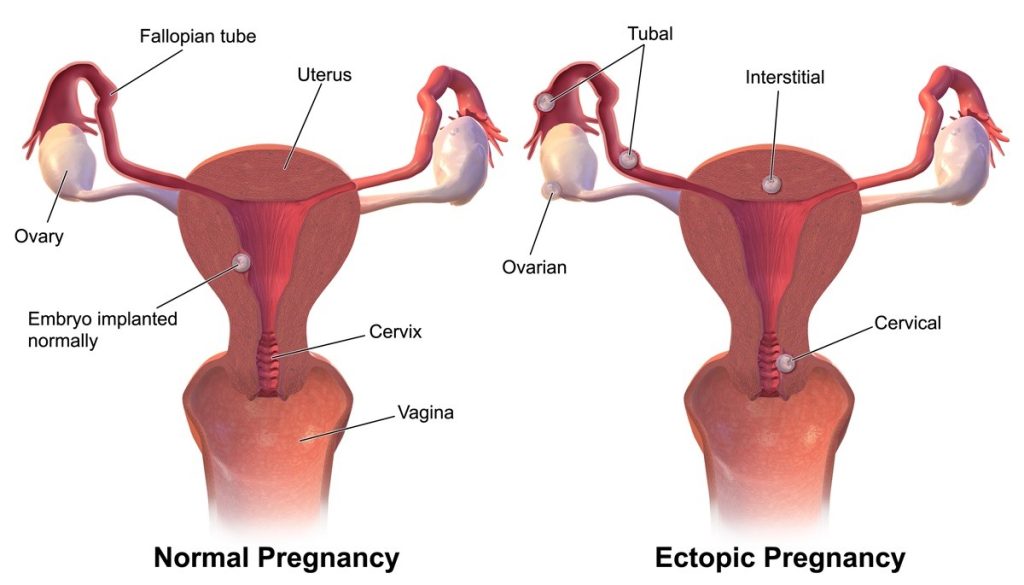
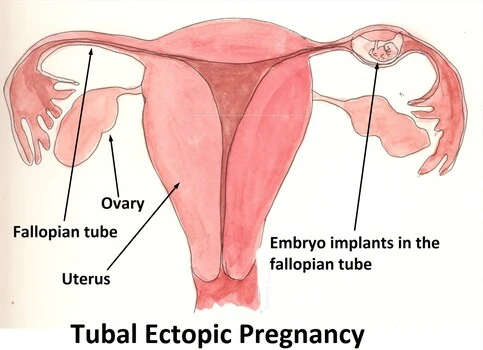
Most commonly an ectopic pregnancy occurs in a fallopian tube or oviduct (which are a pair of tubes that connect ovaries to the uterus), and this type of ectopic pregnancy is known as a tubal pregnancy. More than 95% ectopic pregnancies happen in the fallopian tubes. For that reason, ectopic pregnancies are also commonly known as “tubal pregnancies”.
Less commonly an ectopic pregnancy may occur in parts of the body like:
- Ovaries
- Abdomen
- Cervix (neck) of the uterus
Unfortunately, there is almost no chance for an ectopic pregnancy to succeed.
All types of ectopic pregnancies are bound to fail. Because except the uterus no other organs of the body can provide the right space and the nurturing tissue for the embryo to develop.
If ectopic pregnancy is not detected and managed early, the situation will be life threatening to the mother because as the embryo grows, it will finally burst the organ where it is developing in.
This can cause major internal bleeding and death of the mother. That’s why an ectopic pregnancy has to be diagnosed early and removed using medicines or an operation.
The occurrence of ectopic pregnancy is approximately 2 out of every 100 pregnancies (20 out of 1,000) in North America. Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of death of the pregnant women in the first trimester in the world.
Causes Of Ectopic Pregnancy
Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube and after that normally the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus for implantation. But when the fertilized egg’s movement is slowed down or obstructed / blocked usually because a fallopian tube is infected or inflamed or scarred then the fertilized egg gets implanted in the fallopian tube leading to a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy.
Risk Factors Of Ectopic Pregnancy (Who Is At Risk Of Ectopic Pregnancy?)
An ectopic pregnancy can happen in any woman. But there are several conditions that make a woman more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy. Those conditions are as follows:
- Having a prior history of ectopic pregnancy
- Fallopian tube damage due to pelvic inflammatory diseases (PIDs) such as gonorrhea, syphilis, etc
- Previous tubal/fallopian tube surgery
- Smoking cigarettes
- Having multiple sexual partners
- High maternal age (usually higher than 35)
- Previous abdominal surgery (like appendicectomy, caesarean section, etc)
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Use of medicines to stimulate ovulation
- Use of Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCDs)
- Endometriosis
- Conception on oral contraceptive pills or morning after pills
It is quite possible for you to have an ectopic pregnancy even if you don’t have any of the above risk factors. In reality, approximately one-half of all diagnosed ectopic pregnancies occur in women who do not have any known risk factors.
Signs And Symptoms Of Ectopic Pregnancy
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy varies from woman to woman. Approximately 10% women do not exhibit any specific symptoms of ectopic pregnancy in the beginning, i.e., in 10% cases the early symptoms of an ep are very similar to a typical pregnancy symptoms (such as a missed menstrual period, tender breasts, stomach upset, etc).
Most women develop additional symptoms of ectopic pregnancy in the 6th week of pregnancy. These include:
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pain in lower abdomen, pelvis and lower back (pain may be mainly on one side)
- Dizziness or weakness
At this stage, it may be hard to know if you are experiencing a normal pregnancy or an ectopic pregnancy. If you experience the above symptoms in the early stage of your pregnancy, then you should consult your obstetrician–gynecologist.
As an ectopic pregnancy grows and causes rupture of the fallopian tube, you may experience additional symptoms, such as:
- Severe lower abdominal pain (usually on one side)
- Low blood pressure or hypotension (caused by blood loss)
- Fainting (also cause by blood loss)
- Hypovolemic shock (caused by reduction of blood volume due to blood loss)
- Rectal pressure or pain on defecation
- Shoulder pain
A ruptured fallopian tube can cause heavy internal bleeding which can be fatal to the mother. If you ever develop the above symptoms (of ruptured fallopian tube), you should rush to the emergency room immediately.
How Is An Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stage is difficult, because in most of the women the early symptoms are like those of a typical normal pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy is usually diagnosed at about 4 to 6 weeks of pregnancy. Your doctor will include the following methods to test and diagnose an ectopic pregnancy:
- Pelvic examination: Your doctor can examine your pelvis to test for sensitivity and pain, to figure out if have an ectopic pregnancy.
- Ultrasound scan: You doctor can also use an internal (transvaginal) ultrasound scan to see if the embryo is implanted in the uterus or somewhere else. A transvaginal scan (TVS) may not detect the location of the embryo in the very early stage of the pregnancy. If this is the case, then your doctor will repeat the scan a few days later.
- Blood tests: Your doctor can also perform blood tests to detect changes the level of a pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG). In a normal pregnancy the hCG levels double after a period of every 24 to 48 hours. Low levels of hCG in blood are proof of a problem, like an ectopic pregnancy.
Treatments Of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies are treated either medically (injecting methotrexate) or surgically depending on:
- the medical stability of the woman
- the size of the fetus
- location of the fetus
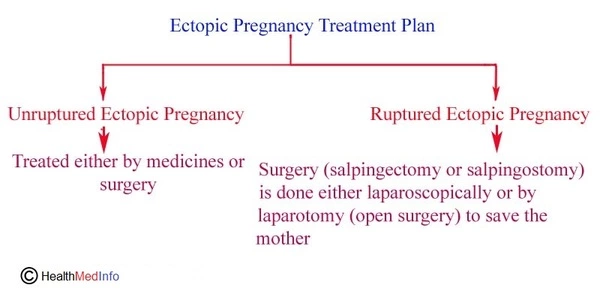
1. Medical Treatment Of Ectopic Pregnancy
If you are diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy in the early stage, your fallopian tubes are not damaged and you have low level of hCG, then you may be managed with medicine. Your doctor can inject methotrexate in your buttock or thigh. Methotrexate will terminate the growth of the embryo leading to its abortion. Then the developing fetus will be either absorbed by your body or pass out with the blood of the menstrual period.
2. Surgical Treatment Of Ectopic Pregnancy
If medical treatment doesn’t work for you and you have high level of hCG, severe symptoms and ruptured fallopian tubes, then surgical intervention is the only option left for you.
Your doctor will perform either laparoscopy (keyhole surgery) or laparotomy (open surgery) to gain access to the affected fallopian tube. Then the doctor will incise the affected fallopian tube and either remove only the fetus (salpingostomy) or remove the affected fallopian tube along with fetus (salpingectomy).
Most patients with ruptured ectopic pregnancy also need immediate resuscitation with intravenous fluids and blood transfusion.
Can You Get Pregnant After An Ectopic Pregnancy?
If your previous EP was treated without removing the fallopian tubes, you still have a reasonable/ good chance to get pregnant and deliver a healthy, full -term baby. You can get pregnant even if one fallopian tube has been removed, provided the other tube is in healthy condition. But while trying to get pregnant again after an EP you have a slightly higher chance of developing another EP. So as soon as you get pregnant in future, you should consult your doctor to confirm that the embryo is growing in the right place (ie, inside uterus)
But if you have experienced several ectopic pregnancies or had both fallopian tubes removed or have fertility disorders, then your doctor would advise you to go for an in vitro fertilization (IVF) or a test tube baby.
Frequently Asked Questions By Patients:
-
How soon would you know if you have an ectopic pregnancy?
If you have developed an ectopic pregnancy, then you may usually (but not always) start experiencing its symptoms (like vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, etc) at about 6 to 8 weeks after the last menstrual period (LMP). However, only a qualified Ob-Gyn can confirm the diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy. So you must consult with your Ob-Gyn as soon as you start experiencing the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
-
Can Ectopic Pregnancies Miscarry On Their Own?
Sometimes an ectopic pregnancy will shrivel, shrink and miscarry on its own. Then it is disintegrated and absorbed the body, and there is no or minimal bleeding or pain. In this case, no medical intervention is required. However, in majority of the cases, ectopic pregnancies rupture and cause severe lower abdominal pain, internal bleeding, hypotension and fainting. In this situation the women must be rushed to the nearest emergency room.
-
Why Does Ectopic Pregnancy Cause Shoulder Pain?
When an ectopic pregnancy bursts it causes bleeding and collection of blood clots in abdomen. This internal bleeding is not visible from outside, but it can irritate the phrenic nerve which supplies the diaphragm. This irritation to the phrenic nerve causes referred pain (pain that is felt at a location different from the injured part) in the shoulder tip. This can occur in one or both shoulder tips.
-
What Does Ectopic Shoulder Pain Feel Like?
Shoulder tip pain due to an ectopic pregnancy may feel like a sudden and very strange pain at the tip of your shoulder, ie, where your shoulder ends and arm starts. This pain is very unusual and it is not similar to a muscular pain. This pain is sudden, sharp and stabbing in nature, i.e., it feels something like someone is poking you sharply from inside out. The intensity of this pain may increase or decrease in sharp waves and changes a little with the changes in your breathing pattern, and it gets worse by breathing deeply.
The intensity of shoulder tip pain increases on lying down. Because on lying down, more blood collects behind the diaphragm causing more irritation to the phrenic nerve. -
Is Ectopic Shoulder Pain In Both Shoulders?
When an ectopic pregnancy ruptures, then the shoulder pain may start. You may experience this peculiar pain in one or both of the shoulders.
References:
- Perkins, Kiran M et al. (2015). Risk of ectopic pregnancy associated with assisted reproductive technology in the United States, 2001-2011.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4315158/ - Dhar, Hansa et al. “Methotrexate treatment of ectopic pregnancy: experience at nizwa hospital with literature review.” Oman medical journal vol. 26,2 (2011): 94-8. doi:10.5001/omj.2011.24
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3191676/ - Ectopic pregnancy. (2017).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Ectopic-Pregnancy


